What is Generative Engine Optimization?

Table of Contents
Toggle1. Marketers Can’t Deny: The Search Landscape is Changing
Generative AI powered search platforms are creating a new reality where users get information without ever leaving the results page. This "zero-click" trend is fundamentally altering the value of traditional website traffic.
Rise of Zero-Click Searches
70%
Projected percentage of Google searches that will be "zero-click" by 2025.
Search Engine Land Report
CTR for #1 Spot Plummets
-34.5%
Average drop in click-through rate for the #1 organic result when an AI Overview is present.
Ahrefs Report
Competitive Advantage
+40%
Early GEO adopters see up to 40% higher visibility in AI responses through strategic optimization.
Writesonic Report
AI Lead Conversion
4.4x
Leads from AI-generated recommendations convert up to 4.4x better than those from traditional search.
AI Monitor Report

2. What are Generative Engines?
Generative Engines? Sounds intense, right? Let’s cut through the noise and break it down.
2.1 Defining Generative Engines?
The way we search for information has been changed by generative engines such as Perplexity, Google’s AI Overview, and ChatGPT. Rather than merely providing you with a list of links, these tools use real-time online data and their profound linguistic knowledge to provide concise, straightforward responses that are nearly identical to an expert’s explanation.
Consider them a hybrid of a search engine and an AI helper. They offer you the information up front rather than just directing you in the wrong direction. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a solution for this. For your material to appear in these AI-powered results, it must be reliable, organized, and in line with user inquiries. GEO, in summary, makes sure that your material doesn’t just exist. It gets seen, cited, and trusted by AI.
2.2 How Generative Engines Work?
Large Language Models (LLMs), which are trained on an enormous amount of books, papers, webpages, and other online information, are the foundation of AI-driven search.1 Through intensive training, LLMs can acquire complex grammatical, contextual, and tonal patterns that enable them to successfully synthesize information and generate responses that resemble those of humans.1 One of these features relies heavily on Natural Language Processing (NLP), which enables these models to understand the context and intent of a user’s inquiry. This allows them to grasp the subtleties of language and provide accurate and pertinent responses. By analyzing full sentences as opposed to individual keywords, advanced natural language processing (NLP) systems like Google’s BERT greatly reduce uncertainties in query interpretation.1
Search engines rely heavily on machine learning to determine what we’re looking for. These algorithms excel at identifying trends in data and can determine whether a user is only seeking information, is prepared to make a purchase, or is attempting to locate a certain website. Advanced methods like supervised and deep learning are used by tools like BERT and GPT to classify these intents with surprisingly high accuracy .1 However, it doesn’t end there. Even if a user hasn’t said what they require directly, AI can infer from previous search activity what they might need.13 Even if we didn’t phrase our inquiry precisely, this type of predictive modeling helps search engines grasp the meaning behind our words, not just the keywords, and beneficial return results.16
Retrieval-Augmented Gen, or RAG for short, is another exciting development. Before formulating a response, it enables AI models to import new, pertinent data from other sources, such as live databases or corporate papers. 15 This helps prevent the common issue of AI occasionally producing inaccurate or out-of-date responses. 18 The way RAG operates is by converting documents into searchable formats, selecting the most pertinent ones, and then feeding that information into the model to provide a more precise, contextually aware response.18
Generative AI tools aren’t built to just stay the same. They’re always learning, constantly updating with new information, which helps them get better at giving more accurate answers as time goes on.¹ This kind of continuous learning lets the system adjust on the fly instead of needing to be retrained from scratch. That said, it’s not perfect. Sometimes, newer data can mess with older understanding of a problem known as “catastrophic forgetting.” Other times, changes in the outside world (what researchers call “distribution shift”) make things harder to keep up with.¹⁹A big part of why these systems are getting smarter is something called a Knowledge Graph. Think of it like a map that shows how different topics or ideas are related to each other. These graphs help AI connect the dots, so answers feel more natural and meaningful.¹⁵There’s also another piece under the hood: embeddings. Basically, they turn language into numbers, kind of like a translation, so machines can compare concepts based on meaning, not just matching words.¹⁷ When you search, the AI looks for the closest match in meaning by comparing these number sets (called vectors). And then there’s prompt engineering, the skill of writing good instructions for the AI. It means giving the model clear context, maybe a format to follow, or rules to stick to, so it gives back something more useful.¹⁷Many newer systems use a mix of approaches. They might start with a fast keyword search to pull relevant stuff, then let the AI figure out the deeper meaning.¹⁷ That combo gives you quick results, but also smarter ones a solid balance of speed and depth.
The rise of direct AI-generated answers and zero-click searches isn’t just a coincidence; it’s the result of how advanced AI search has become. With technologies like natural language processing (NLP), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), continual learning, and semantic understanding working behind the scenes, AI systems can now deliver detailed, contextual responses right on the search results page. This shift has had a clear impact: users are increasingly getting what they need without clicking through to a website, leading to a noticeable drop in organic click-through rates. That’s because large language models (LLMs), powered by NLP, can interpret user intent with impressive accuracy, and when paired with RAG, they can pull in fresh, real-time data to build complete answers on the spot. As these systems continue to learn and evolve, their ability to satisfy search intent directly within the SERP will only improve. The result? Traditional SEO strategies that rely on driving traffic through clicks are becoming less effective. This direct link between AI-generated answers and the decline in organic traffic underscores why businesses now need to rethink visibility and start investing in Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) instead.¹
3. How Generative Engines Work
A visual flowchart explaining the core components and processes of AI-driven search, from user query to the rise of Generative Engine Optimization.
User Query
The process begins when a user enters a search query.
Core AI Processing
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Empowers models to comprehend context and intent, analyzing entire sentences (e.g., Google's BERT) to reduce ambiguity.
2. Machine Learning (ML)
Recognizes patterns to categorize query intent (informational, transactional) and uses predictive modeling to anticipate user needs.
Semantic Understanding
The result of NLP & ML. The engine moves beyond keywords to interpret the deeper meaning and intent of the query.
Response Generation Stage
Enhances LLMs with external, real-time data.
- Index external data into vector embeddings.
- Retrieve relevant documents based on query.
- Augment the prompt with retrieved info.
Large Language Model (LLM)
The core engine, trained on vast datasets. It uses the augmented prompt to synthesize a human-like, comprehensive response.
Guided by: Prompt Engineering (crafting clear instructions).
Knowledge Graphs
Digital structures representing concepts and relationships to enhance semantic search.
Embedding & Similarity Search
Text is converted to numerical vectors (embeddings), which are compared to find conceptually relevant matches.
Hybrid Approaches
Combines traditional keyword search (for broad filtering) with LLM-based methods (for refinement).
Final Output: Direct AI-Generated Answer
The user receives a comprehensive, synthesized answer directly on the search engine results page (SERP).
Impact & Consequence
📉
Rise of Zero-Click Searches
Users get answers without clicking on organic results, causing a decline in click-through rates.
🚀
Need for a New Strategy
Traditional SEO is undermined, creating an urgent need for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
The landscape of Generative Engines is populated by a diverse array of platforms, each with unique features and approaches to information discovery.
3.1 ChatGPT:
ChatGPT has become a major force in how people discover content online, especially for educational and tech-related sites. By November 2024, it had referred traffic to over 30,000 unique domains.²¹ Unlike traditional search, where queries average just 4.2 words, users engage with ChatGPT in full sentences or even paragraphs, with the average prompt hitting around 23 words.²¹Its information retrieval runs on a hybrid system: about 54% of prompts are answered using its internal knowledge base, while the remaining 46% tap into real-time web search (when SearchGPT is enabled).²¹There are also clear demographic differences. ChatGPT’s audience skews younger and more male compared to Google’s broader, more evenly split user base.²¹User intent varies based on whether SearchGPT is active. Without it, prompts tend to focus on purely informational questions, deep dives, how-tos, or conceptual explanations. When SearchGPT is turned on, the range expands to include navigational, commercial, and transactional queries, much more in line with what you’d see on Google. Still, a large chunk of prompts defy easy classification and fall into the “unknown intent” category, likely due to the model’s role in helping users solve complex, multi-layered problems.²²
3.2 Perplexity AI
Perplexity isn’t just another AI tool; it’s built for real-world questions that need solid, trustworthy answers.²³ It searches the live web in real time and gives you direct responses, complete with sources you can actually check.²³ That last part matters especially when you’re dealing with research or business decisions. One thing that sets it apart is how it handles follow-up questions. You don’t have to start from scratch every time it remembers the context, so the flow feels more like a chat with someone who’s actually paying attention.²³You can even narrow your results using “Focus Modes,” which let you search within specific types of content say, academic papers or social media posts depending on what you’re after.²³ That makes it especially useful for students who need credible sources fast, or professionals trying to make sense of a big report or industry trend.²⁴Behind the scenes, Perplexity uses a mix of smart tech: it interprets your question using natural language processing, pulls in fresh data from the web, and runs it through machine learning to deliver an answer — citations and all.²⁴
3.3 Google AI Overview:
Google’s latest AI-powered search experience, called Gemini, takes what Bard started and pushes it further by weaving AI-generated answers right into the search results.⁵ The goal? To make search smarter and more personal by better grasping the meaning and context behind what people are asking.⁵Gemini also supports more natural conversations, users can ask follow-up questions, refine their queries on the fly, and the system keeps up.⁵ One of the standout features is its multimodal search, which means you’re not limited to just typing; you can use images, videos, and even audio as part of your search.⁵In places like India, Gemini’s “AI Mode” gets even more advanced. It uses something called “query fan-out,” where it breaks a complex question into smaller parts and runs multiple searches at once all powered by a custom version of Gemini 2.5.²⁵What’s really changing the game, though, is how AI Overviews (AIO) powered by Gemini are starting to dominate the top of the search results.⁵ Instead of clicking through multiple links, users are often getting the answer right there on the page. And while that’s great for convenience, it’s also leading to fewer clicks on traditional organic search results.
3.4 Microsoft Copilot:
Microsoft 365 Copilot takes a big leap forward in how search works inside organizations. At its core is something called semantic indexing, which basically means it builds a smarter map of your data one that understands meaning, not just keywords.²⁶It taps into Microsoft Graph to figure out how different pieces of information are connected, so when you search for something, it’s pulling results based on actual context, not just matching words.²⁶ What’s also helpful is that Copilot isn’t limited to Microsoft files. Thanks to connectors, it can pull in data from other platforms too, whether that data lives in the cloud or on your company’s servers.²⁶Behind the scenes, this works by turning information into vectors, kind of like coordinates for ideas, which lets the system group together similar concepts.²⁶ So even if you’re not using the exact words, Copilot can still understand what you mean and serve up relevant results. It’s a big shift from traditional search, and it opens the door to asking broader, more natural questions.
3.5 DeepSeek AI:
DeepSeek is an inference-based large language model designed to understand a user’s actual needs and context, without requiring detailed, step-by-step instructions or rigid prompt templates.²⁸ Its architecture features a Mixture of Experts (MoE) design, which smartly activates only the sub-networks needed for a given query, making it more efficient.²⁸ It also uses a robust pure reinforcement learning (RL) pipeline to support reasoning, reducing its reliance on supervised fine-tuning and cutting down overall training costs.²⁸One of DeepSeek’s strengths is its scalability. It supports a massive context window of up to 128,000 tokens, allowing it to handle complex, multi-part tasks with ease. It can also generate long-form outputs up to 32,000 tokens. And perhaps most notably, its inference cost is estimated to be just around 2% of OpenAI’s models, which makes it an impressively cost-efficient option for enterprise use.²⁸
3.6 Grok AI:
Developed by xAI, Grok sets itself apart from other AI chatbots with something unique: direct, real-time access to X (formerly Twitter). That gives it an edge when it comes to surfacing current events, trending topics, and breaking news, without being held back by outdated training data.³⁰But Grok doesn’t stop at just Twitter. Its “DeepSearch” feature expands its reach to the rest of the internet. It performs targeted web searches, pulls in relevant pages in real time, and can even follow links to dig deeper, almost like how a human researcher would explore a topic.³⁰To power that kind of smart search, Grok uses a hybrid indexing system. It combines classic inverted indexes (great for keyword-based lookups) with vector-based semantic indexes, which help it understand the meaning behind words, not just the words themselves.³⁰ On top of that, Grok applies chain-of-thought reasoning similar to the ReAct framework to check source credibility, cross-reference details, and make sense of complex information before delivering a response.³⁰
Table: Key Features and Search Approaches of Leading Generative Engines
| Platform Name | Primary Search Approach | Key Differentiating Features | Underlying AI Technologies | Impact on User Interaction/Content Discovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Conversational Q&A | Avg. 23-word prompts, Hybrid internal/external knowledge, Younger/male demographic | LLMs, NLP | Direct answers, new search intents (problem-solving, brainstorming), specific demographic focus |
| Perplexity AI | Citation-Focused Research | Real-time search, Explicit citations for every response, Focus Modes, Context-aware follow-ups | LLMs, NLP, ML | Quick, verifiable answers, reduced clicks, valuable for academic/professional research |
| Google AI Overview | Search & Multimodal Conversation focused | Direct access to Google’s search Algorithms and user interaction data and capable of Multimodal input (text, image, video, audio), | LLMs (Gemini 2.5), NLP, ML | Immediate, contextually relevant answers, reduced clicks, personalized results |
| Microsoft Copilot | Semantic Indexing for Enterprise | Semantic indexing of organizational data, Microsoft Graph integration, Copilot connectors for third-party data | LLMs, Semantic Indexing, Microsoft Graph | Precise, secure, and personalized information retrieval within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem |
| DeepSeek AI | Inference-Based Reasoning | Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, Pure Reinforcement Learning (RL), Massive context window (128k tokens), High output capacity (32k tokens), High cost-efficiency (~2% OpenAI cost) | LLMs, MoE, Pure RL, Transformers | Understands user intent without explicit prompts, cost-effective for complex tasks, and in-depth report generation |
| Grok AI | Real-time Social Data & Deep Research | Direct real-time access to X (Twitter), DeepSearch (human-like research), Hybrid indexing, Chain-of-thought reasoning, “Fun Mode” | LLMs, MoE | Up-to-date info on current events, comprehensive answers for complex queries, engaging personality |
4. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A New Paradigm for Digital Visibility

The shift in search behavior and AI’s increasing role in information delivery has necessitated a new approach to digital visibility: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
4.1 Defining Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the strategic process of fine-tuning your content so it shows up, gets cited, and is recognized by AI-powered search engines and conversational platforms.¹ It’s all about making sure your work appears in places like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Copilot, and even AI image generators.¹Unlike traditional SEO which focuses on improving your website’s position in search results to drive traffic GEO has a different goal: to become the source that large language models (LLMs) rely on when giving users an answer.¹ That shift changes the game. Now it’s not just about ranking, it’s about being the trusted voice inside the AI interface.³But it doesn’t stop there. GEO also helps increase your overall visibility within AI systems, build stronger brand awareness, and indirectly drive more organic traffic by boosting recognition and credibility.¹ And when your content is accurate, helpful, and easy to surface, it improves user satisfaction not just on your site, but across the AI tools people are using every day.
Who Coined the Term Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Vishvak Murahari
Princeton University
Princeton, USA
murahari@cs.princeton.edu
Pranjal Aggarwal
Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
New Delhi, India
pranjal2041@gmail.com
Tanmay Rajpurohit
Independent
Seattle, USA
tanmay.rajpurohit@gmail.com
Ashwin Kalyan
Independent
Seattle, USA
asaavashwin@gmail.com
Karthik Narasimhan
Princeton University
Princeton, USA
karthikn@princeton.edu
Ameet Deshpande
Princeton University
Princeton, USA
asd@princeton.edu
5. SEO vs. GEO: A Fundamental Shift
Traditional SEO
The goal is to rank high on a results page to drive users to your website.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
The goal is to become a cited source within the AI's direct answer.
Table: Showing difference between SEO & GEO on different parameters
| Parameters | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank higher in traditional search engine result pages (SERPs) | Be cited and featured in AI‑generated summaries (ChatGPT, Google AI Overview, Perplexity AI) |
| Target Engines | Google, Bing, Yahoo | Generative engines: Google AI overview, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Bing AI |
| Content Focus | Keyword-rich content, backlinks, and on-page optimization | Context-rich, structured, AI‑readable content that machines can understand and cite |
| Technical Strategies | Meta tags, sitemaps, crawlability, URL structure | Schema, conversational Q&A formatting, [llms].txt, AI‑crawlable structures |
| Measurement Metrics | Rankings, organic traffic, click-through rate (CTR) | Citation frequency in AI answers, presence in summaries, and AI‑driven referral traffic |
| Optimization Tools | SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, Google Search Console | AI‑specific tools: AI Monitor, BrandRank.ai, Otterly.ai—tracking mentions and sentiment in generative engines |
| Typical Outcome | More clicks, higher page views, improved SERP visibility | Direct answer inclusion, zero‑click content display, and increased brand visibility within AI responses |
The Great Disconnect: Why Good SEO Isn't Enough
A high Google ranking no longer guarantees visibility in AI answers. AI models use different criteria to source information, prioritizing structure and verifiability over traditional ranking signals.
Top 10 Google Results vs. AI Citations
Only 20% of pages ranking in the top 10 are consistently cited in AI-generated responses.
What Explains AI Citation Behavior?
A staggering 95% of AI citation behavior cannot be explained by traditional SEO metrics like traffic or backlinks.
🚀 Key Impacts of GEO on Digital Marketing
| Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Search Visibility | Instead of ranking #1 on Google, GEO helps your content appear directly in AI-generated answers and summaries. |
| Traffic Sources | More traffic now comes from AI-driven referrals (e.g., Perplexity citations, Google AI source links) than traditional search clicks in many niches. |
| Brand Authority | Being cited by LLMs positions your brand as a trustworthy expert in your domain, similar to getting quoted by the media. |
| Content Strategy | Forces a shift from keyword stuffing to context-rich, AI-readable content designed for understanding, not just ranking. |
| Competitive Edge | Early GEO adopters are gaining ground in emerging search channels while others are still focused solely on outdated SEO tactics. |
6. Challenges Marketers Face While Doing GEO
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) offers immense potential, but it comes with its own set of unique challenges that marketers must overcome.
1. Lack of Transparency in Generative Algorithms
Unlike traditional search algorithms, LLMs operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand their internal reasoning for prioritizing and citing content.
It's hard to pinpoint: What sources do they prioritize? How do they decide what to cite? Why is certain content surfaced?
Solution: Structure for Clarity
Structure your content with clarity and semantic relevance. Actively monitor AI tools like Perplexity to observe which sources are being cited and analyze their characteristics.
- ✓Clear semantic relationships
- ✓Consistent entity definitions
- ✓Observe AI citation patterns
2. Decline in Traditional Traffic
With AI providing instant answers, users often experience "zero-click" interactions, leading to fewer website visits even for top-ranking content.
Website Traffic Trend
Traffic numbers can drop overnight, even when content holds a top spot in traditional SERPs.
Solution: Redefine Visibility
Shift your attention from just tracking page views to actively measuring brand visibility and citation presence in AI-generated answers. It’s not just about being seen—it’s about being mentioned.
- ✓Measure AI citation frequency
- ✓Track brand mentions in AI responses
- ✓Focus on influence over clicks
3. Constantly Evolving AI Models
Generative engines are in their early stages and evolving rapidly, causing strategies for content visibility to shift just as quickly.
What earns your content a citation this week might be overlooked the next. Staying relevant requires continuous monitoring.
Solution: Stay Flexible & Adaptive
GEO is not a one-time task. Stay flexible with your plan, spot new trends fast, and refresh your content pieces before they go stale.
- ✓Implement agile GEO strategies
- ✓Proactive trend spotting
- ✓Regular content audits & refreshes
7. Top Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Optimization Techniques
To stand out in AI-powered search, you need more than traditional SEO—it’s about crafting content that AI finds credible, relevant, and reference-worthy. These proven techniques focus on enhancing your brand’s chances of being cited directly in AI-generated answers, where trust and context matter more than ever. Some of the strategies that we would vouch for are:
1. Optimize AI-Bot Crawlability
Ensure AI crawlers (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini) can access and understand your site.
Key actions:
- Do not disallow crawlers in the robots.txt file
- Fast load times + mobile optimization
- Fix crawl errors (e.g., broken links)
- 63% of websites fail core crawlability criteria.
2. Strengthen Reviews on Platform Ecosystems
AI models prioritize reviews from trusted platforms.
Key actions:
- Try to increase authentic reviews on platforms like Yelp, G2, or niche platforms
- Focus on products/services with detailed feedback
- Keep an eye on the reviews and respond when needed to stay credible.
3. Join Niche Communities (e.g., Reddit)
Generative engines value authentic community discussions.
Key actions:
- Pick the right subreddit or forum, share helpful tips, and skip the hard sell so you don’t come off like spam.
- Foster discussions about your brand/products
- Encourage upvotes and shares to boost visibility
4. Build Credibility with Citations and Credible Content
AI favors trusted, well-sourced content.
Key actions:
- Cite reputable sources (studies, expert journals, or articles from authors who are well-known in your field).
- Include expert quotes/contributions
- Publish original research or in-depth analysis
5. Expand Contextual Relevance via Semantic Keywords
Optimize for natural language queries, not just keywords.
Key actions:
- Target long-tail, conversational phrases
- Group-related terms (semantic clusters)
- Cover topics comprehensively (“topic clusters”)
6. Content Optimization for GEO
Success in GEO is built on a foundation of technical excellence, structured content, and demonstrable authority. The goal is to make your content not just discoverable, but easily extractable and trustworthy for AI models.
The Pyramid of GEO Authority
53%
More likely to be cited by AI
when content includes structured data (Schema.org).
Create Extractable Content
- ✓Comparison Tables
- ✓Numbered Lists & Processes
- ✓FAQ Sections with Schema
- ✓Executive Summaries (TL;DR)
7. Leverage Traditional PR & Branding
Offline visibility fuels AI training data.
Key actions:
- Secure press coverage in industry publications
- Publish thought leadership (e.g., whitepapers, webinars)
- Boost brand mentions across credible sites
For a deeper dive into the techniques that would help you out with Generative Engine Optimization, check out the full article: 👉 Top 11 Generative Engine Optimization Techniques – AI Monitor
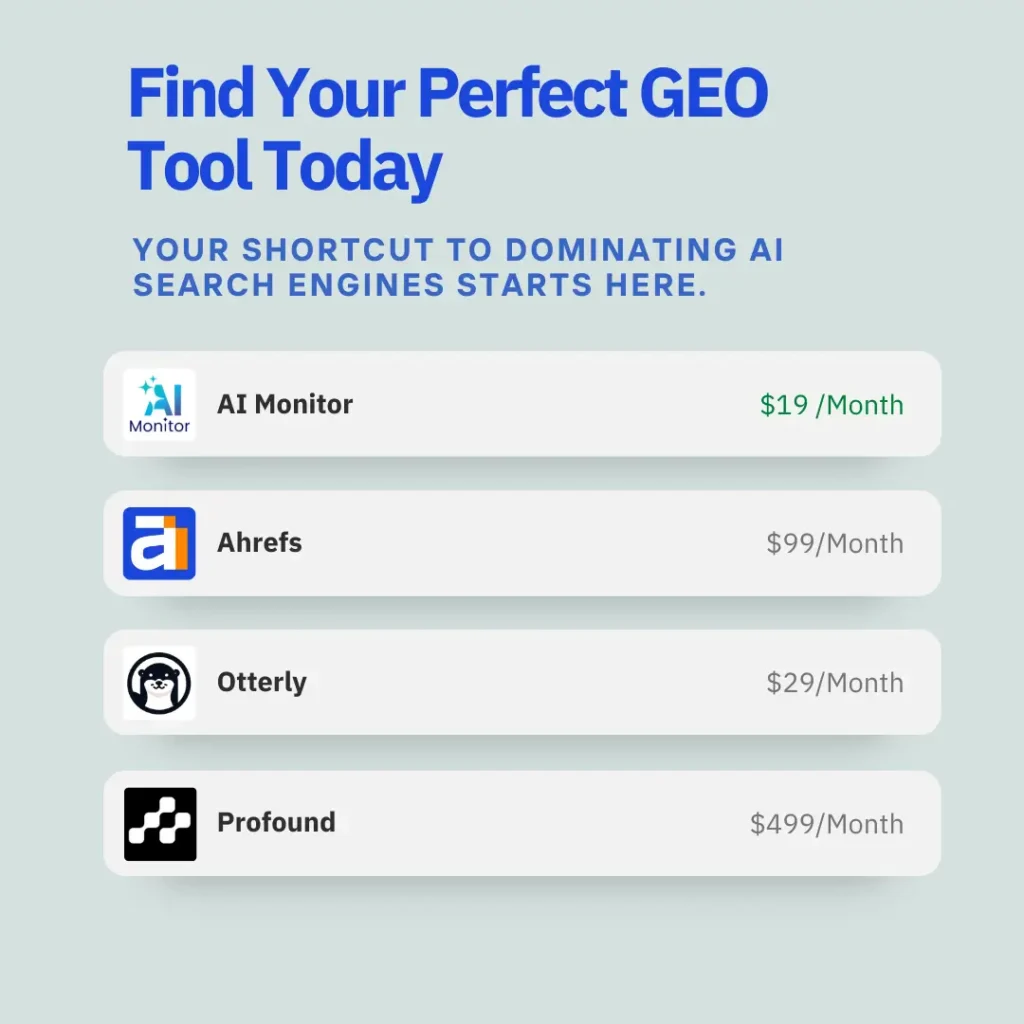
8. Tools That Enhance the Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Process
Your essential toolkit for winning in AI-powered search
As AI-generated answers become the new front door to the internet, GEO is changing how brands appear in tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and more. But executing a strong GEO strategy requires more than just great content, it requires the right tools.
Here’s a curated list of powerful GEO tools shaping the future of AI visibility in 2025:
AI Monitor offers real-time tracking of your brand’s visibility in AI search platforms such as Google’s AI Overview, ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity.
It monitors prompts, sentiment, citations, and competitive keyword coverage, making it the most complete and useful GEO platform on the market.
✅ Used by top agencies to drive 500%+ visibility gains.
Semrush rolled out GEO-friendly tweaks like prompt tracking and AI-answer detection. It’s a smooth way for traditional SEO professionals to integrate GEO without rebuilding their stack.
💡Starter plans kick off at $99/month.
Otterly.AI is an affordable tool that provides basic prompt visibility and keyword-to-prompt matching.
It’s easy to use and offers fast setup, though results can be inconsistent.
💸 If you’re in the early stages of testing geo-targeted campaigns, this approach pays off.
Profound delivers high-end AI behavior mapping, brand risk forecasting, and prompt-level insights for large organizations.
If you need deep analysis and long-term strategy planning, this is your tool.
📊 Requires premium licensing and advanced onboarding.
BrandRank.ai offers a hybrid approach: AI monitoring paired with human review to detect brand misrepresentation or legal risk in generative answers.
🔒 Especially valuable for finance, healthcare, or government orgs.
Ziptie.dev is a developer-first API toolkit for tracking generative engines at a technical level.
You can build your dashboards, alerts, and pipelines to follow brand, product, or keyword prompts as they evolve.
⚙️ Ideal for custom solutions and AI research.
Did you know there are over 50+ GEO tools already shaping the future of AI-driven search?
We’ve put together a curated list of the most powerful Generative Engine Optimization tools on the planet, your one-stop resource to stay ahead in the game.
Got a GEO tool we haven’t included yet? Drop us an email, and we’ll make sure it gets the spotlight it deserves
9. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Pros vs. Cons
| Aspect | Pros (Advantages) | Cons (Challenges) |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | ▶️ Appears in AI-generated answers (e.g., Google SGE, Perplexity), capturing users before they click links. | ▶️ Traffic cannibalization: Fewer clicks to websites if the answer fully satisfies users in the AI snippet. |
| Authority Building | ▶️ Source attribution (e.g., "According to [Your Site]") boosts brand trust and E-E-A-T. | ▶️ Zero control over how generative engines summarize/represent your content. |
| Content Strategy | ▶️ Rewards comprehensive, well-structured content (not keyword stuffing). | ▶️ Requires significant content restructuring: Depth > brevity, multi-perspective coverage. |
| Future-Proofing | ▶️ Prepares for AI-dominated search (25–60% of queries may use generative results by 2026). | ▶️ Rapidly evolving landscape: GEO tactics may become obsolete quickly as AI models update. |
| ROI & Traffic | ▶️ High value for complex, research-driven queries (e.g., comparisons, guides). | ▶️ Unclear monetization: Harder to track conversions if users stay in the AI interface. |
| Technical Execution | ▶️ Less reliance on backlinks vs. traditional SEO. Focuses on content quality. | ▶️ Opaque ranking signals: Lack of clear guidelines (vs. Google's SEO standards). |
| Competition | ▶️ Early-mover advantage: Fewer sites actively optimize for GEO. | ▶️ Dominated by established authorities (e.g., governments, universities, major publishers). |
| User Experience | ▶️ Drives content toward user intent and problem-solving. | ▶️ Forces creators to prioritize AI readability over human engagement (e.g., emotional hooks). |

Do You Know What ChatGPT is Saying about Your Brand?
Don’t wait for a crisis. Proactively manage your brand’s reputation in the age of AI. To learn what AI is saying about you, book 1:1 Meeting with the #1 GEO Expert in the world.
10. How You can Learn Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
As AI-driven search transforms how content is discovered, learning Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) isn’t just optional, it’s essential for marketers, creators, and SEO professionals who wish to stay ahead of the curve.
But where do you start?
That’s exactly why we’ve created a free, in-depth course—designed to take you from GEO beginner to expert, even if you’re not technically inclined or deeply familiar with how AI works. It breaks down complex concepts into practical, actionable steps to help you succeed in the AI-powered search landscape.
🎓 What You'll Learn:
– How AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity source and surface content
– What makes content “AI-citable” in zero-click summaries
– The tools, techniques, and frameworks that top brands use to rank in generative answers
– Real-world case studies and prompt-based visibility strategies
Whether you’re in SEO, content marketing, or digital strategy, this course will give you the GEO fundamentals and advanced tactics to thrive in the AI-first web.
👉 Start learning here (free):
https://getaimonitor.com/best-generative-engine-optimization-geo-course-for-free/
11. Our Prediction on GEO 🔮
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is no longer a futuristic concept, it’s the foundation of digital visibility in an AI-first search ecosystem. With platforms like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Perplexity providing direct answers before users even click a link. Brands that fail to adapt risk becoming invisible. Just as businesses that ignored the SEO bandwagon in the early 2000s faded from traditional search, those overlooking GEO today will be left behind in AI-generated results.
By 2026, we expect 40–60% of all discovery traffic to come from generative engines, not traditional SERPs. Prompts will replace keywords, and earning citations from AI models will become the new gold standard of authority. It won’t be about ranking on page one, it’ll be about being the trusted source AI draws from.
Real-time monitoring, prompt-aware content, and semantic depth are the building blocks of tomorrow’s digital strategy. GEO isn’t a trend, it’s the next era of search. The brands that act now will shape it. The ones that don’t? They’ll be searching for relevance in a landscape that’s already moved on.
Works Cited
1. Generative Engine Optimization: Everything You Need to Know …, accessed July 02, 2025,
https://mangools.com/blog/generative-engine-optimization/
2. SEO vs GEO: Understanding the Key Differences in 2025 …, accessed July 08, 2025,
https://boomcycle.com/blog/seo-vs-geo-understanding-the-key-differences/
3. GEO vs SEO: Do Traditional Tactics Still Matter in AI Search? |, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.digivate.com/blog/ai/geo-vs-seo-do-traditional-tactics-still-matter-in-ai-search/
4. How Artificial Intelligence Is Used in Search Engines | Gisma, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.gisma.com/blog/how-ai-is-transforming-search-engines
5. How Google Gemini Is Affecting Search as We Know It, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.vimarketingandbranding.com/how-google-gemini-is-affecting-search-as-we-know-it-2/
6. How Google’s AI Overview impacts your organic traffic (and what you can do about it), accessed July 01, 2025,
https://seeders.com/blog/how-googles-ai-overview-impacts-your-organic-traffic-and-what-you-can-do-about-it/
7. Survey: 83% of users prefer AI search over ‘traditional’ Googling – Innovating with AI, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://innovatingwithai.com/is-ai-search-replacing-traditional-search/
8. How AEO Can Help With Zero-Click Searches: Reclaiming Visibility in 2025 – Single Grain, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.singlegrain.com/digital-marketing-strategy/how-aeo-can-help-with-zero-click-searches-in-2025/
9. Similarweb: No Clicks From Google Grew From 56% to 69% Since AI Overviews, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.seroundtable.com/similarweb-google-zero-click-search-growth-39706.html
10. 5 ways AI helps boost your site’s E-E-A-T score: Higher rankings in 2025 – Outranking, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.outranking.io/blog/ways-ai-helps-boost-your-sites-e-e-a-t-score/
11. Creating Helpful, Reliable, People-First Content | Google Search Central | Documentation, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/creating-helpful-content
12 The Future of SEO: How AI Is Already Changing Search Engine …, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://researchfdi.com/future-of-seo-ai/
13. Understanding How to Identify User Search Intent Using AI – Nurix AI, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.nurix.ai/blogs/user-search-intent-ai
14. LLM Search Optimization: The Executive’s Guide to Success – Brand Audit Services, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://brandauditors.com/blog/guide-to-llm-search-optimization/
15. LLM Search Engines: AI-Driven Information Retrieval – ClickUp, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://clickup.com/blog/llm-search-engine/
16. Contextual Search vs Traditional Search: Explore Key Differences – Wizzy.ai, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://wizzy.ai/blog/contextual-search-vs-traditional-search/
17. How Do You Search a Long List with LLM? Techniques & Tips, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://blog.promptlayer.com/how-do-you-search-a-long-list-with-llm-large-language-models/
18. Retrieval-augmented generation – Wikipedia, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retrieval-augmented_generation
19. Lifelong Learning in Generative AI Models – [x]cube LABS, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.xcubelabs.com/blog/lifelong-learning-and-continual-adaptation-in-generative-ai-models/
20. Knowledge graph – Wikipedia, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knowledge_graph
21. The ChatGPT effect on web traffic and shifting search patterns …, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.okoone.com/spark/marketing-growth/the-chatgpt-effect-on-web-traffic-and-shifting-search-patterns/
22. Investigating ChatGPT Search: Insights from 80 Million Clickstream …, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.semrush.com/blog/chatgpt-search-insights/
23. A Complete How-To Guide to Perplexity AI – Learn Prompting, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://learnprompting.org/blog/guide-perplexity
24. What is Perplexity AI? How it Works, Key Features, Use Cases …, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.getguru.com/reference/what-is-perplexity-ai-and-how-to-use-it
25. “We want to make Search so effortless you can ask anything:” As AI Mode launches in India, Google explains how it moves beyond traditional search, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/technology/tech-news/we-want-to-make-search-so-effortless-you-can-ask-anything-as-ai-mode-launches-in-india-google-explains-how-it-moves-beyond-traditional-search/articleshow/122322495.cms
26. Semantic indexing for Microsoft 365 Copilot | Microsoft Learn, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftsearch/semantic-index-for-copilot
27. Microsoft 365 Copilot connectors overview for Microsoft Search, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftsearch/connectors-overview
28. Everything About DeepSeek: Key Features, Usage, and Technical …, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.popai.pro/resources/everything-about-deepseek/
29. DeepSeek: Unique Features, Potential Pitfalls, and Adoption Strategies for Organizations | by Gelareh Taghizadeh | Medium, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://medium.com/@gelareh.taghizadeh_63525/deepseek-unique-features-potential-pitfalls-and-strategic-implementation-for-organisations-b55e5f016b81
30. Understanding Grok: A Comprehensive Guide to Grok Websearch …, accessed July 05, 2025,
https://www.tryprofound.com/blog/understanding-grok-a-comprehensive-guide-to-grok-websearch-grok-deepsearch
31. Grok AI Explained: A Simple Guide to Elon Musk’s AI Assistant …, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://securityboulevard.com/2025/04/grok-ai-explained-a-simple-guide-to-elon-musks-ai-assistant/
32. Google SGE Organic Traffic Impact Divided By Verticals [Data Study], accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-sge-organic-traffic-impact-divided-by-verticals/514800/
33. Traditional Search vs. AI Search… Which one do you think is better? : r/Futurism – Reddit, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.reddit.com/r/Futurism/comments/1j48idu/traditional_search_vs_ai_search_which_one_do_you/
34. What’s Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) & How To Do It – Foundation Marketing, accessed July 09, 2025,
https://foundationinc.co/lab/generative-engine-optimization
35. A beginner’s guide to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) – Aspectus Group, accessed July 02, 2025,
https://www.aspectusgroup.com/insights/a-beginners-guide-to-generative-engine-optimization-geo/
36. Google AI Mode vs. Traditional Search & Other LLMs [Study] – Semrush, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.semrush.com/blog/ai-mode-comparison-study/
37. 19 SEO Case Studies to Improve Your Strategy in 2025 – AIOSEO, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://aioseo.com/seo-case-studies/
38. Top 10 SEO AI Use Cases with Case Studies in 2025 – Research AIMultiple, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://research.aimultiple.com/seo-ai/
39. Understanding Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A New Era for SEO – Medium, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://medium.com/@info_92521/understanding-generative-engine-optimization-geo-a-new-era-for-seo-695deec88c3d
40. Ethical Challenges in AI-Powered Search Engines – Creaitor, accessed July 01, 2025,
https://www.creaitor.ai/blog/ai-powered-search-and-its-challenges
41. Ethics & AI – Artificial Intelligence (Generative) Resources – Guides at Georgetown University, accessed July 10, 2025,
https://guides.library.georgetown.edu/ai/ethic